
Children & Podiatry

CHILDREN’S FOOT DEVELOPMENT
- alt 12 months: The foot is made up of mostly cartilage and has doubled its size since birth. Children should have started to play with their own feet by this age and wear socks for warmth and protection but no shoes.
- Kinder Age:Kinder Age: Children should be learning to jump, skip, hop, kick a ball and improving running skills. Shoes should offer protection but still allow freedom and mobility and have adjustable straps or laces.
- School Age: The feet take on a grown up appearance and their walking starts to resemble that of an adult. Teaching them to tie shoe laces at this age is really important. Also keeping their feet clean and dry and wearing thongs around the pool is important to prevent warts and tinea.
COMMON PROBLEMS WITH CHILDREN’S FEET
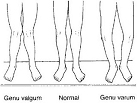
- Knock Knees (Genu Valgum):A curvature of the legs that causes the knees to touch whilst the feet are apart. This can be due to the bone’s structure, muscle abnormalities and some children can go through this as part of their growth and development. It can cause problems if not monitored and treated before age seven when it becomes fixed.
- Bow Legs (Genu Varum):Opposite of knock knees it is a curvature of the legs that leaves a larger than normal gap between the legs. After infancy this deformity is not normal and should be checked.
- Flat Feet: This is where the arch in the instep has dropped. In babies this is normal as the arch in their foot has not yet developed. However this may persist into adult hood and cause problems such as difficulty running for long distances, extra stress on joints, muscles and ligaments resulting in injuries or pain
- High Arched Feet:The opposite to flat feet. This can be genetic or caused by an underlying neurological condition. It means the outside of the takes excessive pressure and this can result in pain. It can also be difficult to fit shoes and makes the foot shorter.
High Arched Feet: The opposite to flat feet. This can be genetic or caused by an underlying neurological condition. It means the outside of the takes excessive pressure and this can result in pain. It can also be difficult to fit shoes and makes the foot shorter.
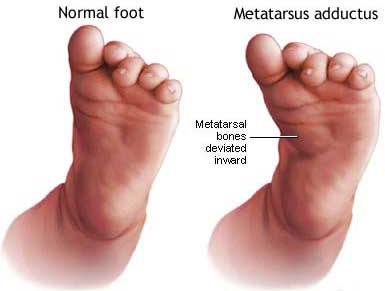
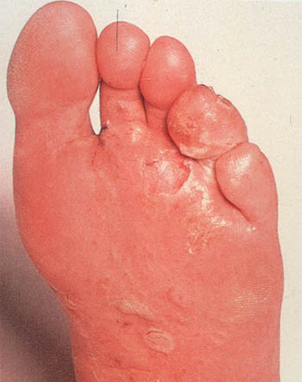
Balance& Walking Difficulties: Difficulty in balancing can be caused by underlying problems such as instability in the ankles, high arched feet and developmental differences. Some of the problems treated at Complete Feet are:
In-toeing: This is where the child walks and stands with their feet turned inwards. If it doesn’t resolve with age then it can lead to other problems in adult hood.
Knee Pain: If the alignment of the ankles is not correct then this may affect the knees- especially at the knee cap. This may lead to pain and undue wear of the patello-femoral joint.
Severes Diease: the growth plate in the heel becomes inflamed and painful. This can be successfully treated with Orthotic therapy.
Ligament problems: some children can develop pain due to sports or activity as a result of poor foot posture. A biomechanical assessment of the childs feet by a Complete Feet professional will diagnose the problem and treat the cause.


